Depression is the second most common mental health disorder, trailing closely behind anxiety. It affects approximately 280 million people across the globe (3.8% of the entire world’s population).[1]
Characterized by a chronic feeling of sadness, lack of interest in previously enjoyed activities, and a marked decrease in energy levels, depression can substantially impair an individual’s day-to-day functionality and quality of life.[2] In some cases, depression can even prove fatal, contributing to death via suicide.
Despite being so prevalent, depression is often misunderstood.
It is actually a group of conditions differentiated by unique symptoms, causes, and implications—not one single disorder.
Therefore, any therapist or mental health practitioner wishing to effectively work with depression must have a comprehensive understanding of its various forms.
In this article, we’ll provide a thorough exploration of depression, its varied types, the critical role of treatment plans, and how to develop a treatment plan. We also discuss how modern software platforms, like Quenza, can aid in creating and managing treatment plans efficiently and effectively.
Understanding Depression: The Different Types
Depression manifests in a variety of forms, each carrying distinct characteristics and requiring different treatment approaches.
The table below gives a brief overview of the most common depressive disorders described in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®).
| DEPRESSION SUBTYPE | BRIEF OVERVIEW |
|---|---|
| Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) | One of the most prevalent forms of depression. Typified by a constant low mood, significant loss of interest in activities that the individual previously found pleasurable, sleep disturbances, changes in appetite, feelings of intense guilt or worthlessness, difficulty in concentrating, and recurrent thoughts of death or suicide. |
| Persistent Depressive Disorder (PDD) | A more chronic form of depression, with its symptoms enduring for at least two years. Although the symptoms may be less severe than MDD, they are often longer-lasting, making it a chronic condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life over time. |
| Bipolar Disorder | Previously referred to as manic depression, bipolar disorder is another type of depression marked by severe mood swings, ranging from depressive lows to manic highs. Individuals suffering from bipolar disorder often experience periods of normal mood interspersed between these episodes, making it distinct from other types of depression. Also has its own subtypes. |
| Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) | SAD most commonly occurs during winter months when there is less natural sunlight, leading to depressive symptoms that dissipate with the onset of spring and summer. This form of depression is often associated with overeating, oversleeping, low energy, low mood, and weight gain. |
| Perinatal Depression | Formerly known as postpartum or postnatal depression, perinatal depression is a specific type of depressive disorder that can occur during pregnancy or within the first few weeks following childbirth. This type of depression can have profound impacts on both the mother and child, and it’s essential to identify and treat it promptly. |
| Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD) | Another form of depression that exclusively affects women. This severe form of premenstrual syndrome leads to significant depression, irritability, and tension before menstruation. |
| Adjustment Disorder | While not a true depressive illness, adjustment disorder (also called “situational depression”) is a short-term, stress-related condition that arises following a significant life-changing event or stressful period. This type of depression tends to resolve within a few months, but can develop into a more severe form of depression if not addressed adequately. |
Treatment Plans: An Overview
A depression treatment plan is:[3]
A comprehensive strategy devised by mental health professionals to effectively manage a patient’s depressive symptoms.
These plans are usually individualized to cater to the unique needs and circumstances of each patient. It serves as a blueprint outlining the interventions that will be employed, the specific goals to be achieved, and a timeline for progress evaluation.
Treatment plans generally begin with a diagnostic assessment, employing tools like the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) to gauge the severity and nature of the depressive symptoms.[4] This assessment (or a similar standardized and validated tool), coupled with an in-depth understanding of the patient’s medical and personal history, assists in formulating an effective plan.
Defining Objectives
The treatment plan should clearly define the objectives or goals of depression treatment.
Goals are often guided by the SMART criteria…
- Specific
- Measurable
- Achievable
- Relevant
- Time-bound
…to ensure they are realistic and attainable.
For instance, a goal could be reducing the severity of a particular depressive symptom, by a specific amount, within a defined period.
Detailing Interventions
The plan also delineates the interventions to be used to achieve treatment goals.
These could include one or a combination of:
- Pharmacological (medication) treatments
- Psychotherapy or counseling
- Lifestyle changes
- Behavioral interventions
- Social support
- In cases of treatment-resistant depression, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) or other brain stimulation therapies [4]
The choice of intervention often depends on the severity and type of depression, patient preference, and the potential for side effects or other complications.
Outlining the Timeframe
Finally, the treatment plan includes a timeline that sets an approximate duration for the treatment and establishes a framework for evaluating progress.
It is important that both the patient and therapist understand that this timeline is flexible and can be adjusted based on the patient’s response to treatment.
Individualized Goals
The overall goal of any depression treatment plan is to alleviate the symptoms of depression and improve the patient’s overall quality of life.
However, each person’s experience of depression is unique. So depression treatment plans should always include individualized goals based on the patient’s circumstances, needs, and desires.
These individualized goals often represent specific areas of a person’s life that are especially affected by depression, like energy levels or mood. They also might include specific risk factors or triggers, like stress or alcohol misuse.
Some common individualized goals in depression treatment plans include:
- Improving sleep quality
- Engaging in social activities
- Dealing with anxiety or low self-esteem
- Keeping a mood diary (or mood tracking app)
- Reducing stress levels
- Increasing physical activity
- Enhancing nutrition
- Managing comorbid health conditions
- Working on relationship issues
These goals align with a holistic approach to managing depression, addressing both mental and physical health components.
Another important goal in a treatment plan for depression is to reduce the risk of relapse. This involves equipping patients with strategies to cope with future stressors and recognize early signs of a depressive episode.
A Guide to Interventions for Depression
The treatment of depression is multifaceted and usually involves a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions.
Practitioners should strive to develop plans based on a client’s choices and preferences. But keep in mind, because of the impact of the condition, people in the throes of depression aren’t always forthcoming with ideas and strategies to start their recovery.
Therefore, as a medical practitioner, you might have to be a little more prescriptive and assertive than when treating other conditions, especially in the early stages. When you do, however, just make sure to keep your clients’ needs at the core of your intention. Counselors and coaches will still follow their overarching approach to not be prescriptive while allowing the client to lead their path to recovery. In that case, they might start by detailing some simple coping strategies for their clients to give those clients some headspace.
Depression Treatment Plan Interventions
We provided a list of several of these interventions already. But below is a more detailed explanation of each.
Pharmacological treatments
Antidepressant medications are a very common depression treatment.
These include several different, but related classes of drugs, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs).
Each class of antidepressants works differently, and the ideal choice depends on the patient’s symptoms, side effect profiles, and personal preferences.
Psychotherapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective forms of psychotherapy for depression. It helps patients identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to depressive symptoms.
Interpersonal therapy (IPT) is another form of psychotherapy often used, focusing on improving the quality of a patient’s relationships and social functioning to help reduce depressive symptoms (Cuijpers et al., 2014).[5]
Lifestyle interventions
Regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, good sleep hygiene, and avoidance of alcohol and illicit substances are all crucial in managing depression. Regular exercise, in particular, has been shown to have a powerful antidepressant effect.[6]
Alternative therapies
Techniques like mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and acupuncture may also be beneficial for some people with depression.[7] These practices can also usually be safely combined with interventions like medications and psychotherapy.
Example of a Depression Treatment Plan
Let’s look at an example treatment plan for Jeremy, a middle-aged adult recently diagnosed with Major Depressive Disorder.
Jeremy’s treatment plan begins with a comprehensive assessment of his symptoms, using a standardized assessment tool and a detailed exploration of his medical and personal history.
The first goal in Jeremy’s treatment plan is to reduce the severity of depressive symptoms, as measured by a 50% reduction in his PHQ-9 score within the next three months.
Specific interventions to achieve this goal include:
- Starting an antidepressant medication like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which are known to be effective in treating MDD.[8]
- Improve Jeremy’s sleep quality. Sleep disturbances are common in MDD and can be addressed through a combination of good sleep hygiene practices and cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (Irish et al., 2015).[9]
- Enhance social engagement. Individuals with MDD often isolate themselves. Strategies Jeremy identified to address this include joining a support group for men suffering from depression and reaching out to some friends he used to play football with.
The plan also includes Jeremy having fortnightly follow-ups with his primary care doctor to evaluate his progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Jeremy is also provided with education about the nature of MDD and strategies to manage symptoms, aiming to improve self-efficacy and resilience.
Depression Treatment Plan Template
A standard template for a depression treatment plan typically includes the following sections:
Patient Identification: This includes basic demographic information about the patient, such as name, age, and contact information.
Diagnosis: This section provides the specific type of depression that the patient has been diagnosed with and any related conditions.
Assessment Summary: A brief overview of the patient’s symptoms, as well as any relevant medical or personal history.
Treatment Goals: These are the specific, measurable goals that the treatment plan aims to achieve.
Interventions: An outline of the specific interventions that will be used to achieve each goal. This could include medications, psychotherapy, lifestyle changes, and more.
Progress Evaluation: This includes a timeline for when progress will be assessed and the metrics that will be used to gauge progress.
Contingency Plans: This outlines what steps will be taken if the initial treatment plan is not effective and/or the client is exhibiting concerning or risky behavior (e.g., suicidal ideation).
Best Software for Depression Treatment Plans
Advancements in technology have led to the development of various software applications designed to assist clinicians (and clients) in the creation, implementation, and evaluation of depression treatment plans.
Here are 4 examples:
| TheraNest | With options for Lite, Professional, and Enterprise users, TheraNest is a full-featured practice management solution. It includes a treatment plan feature that allows clinicians to create individualized treatment plans, set measurable goals, and track progress over time. |
| SimplePractice | SimplePractice is designed for therapists providing in-person, virtual, or combined depression treatment. It offers customizable treatment plan templates and allows clinicians to easily monitor and update treatment goals. |
| TherapyNotes | Branded as “The most trusted EHR for behavioral health,” TherapyNotes offers robust treatment planning features, allowing clinicians to develop comprehensive treatment plans, track progress, and update plans as needed. |
| Quenza | Quenza has a unique approach to depression treatment plans. Our app and digital platform include all the essentials to run your therapy or coaching practice, like secure notes and messaging facilities. We’ve paired this with an innovative library of 250+ evidence-based Expansions that you can use to build individualized depression treatment plans for your clients in no time. We’ll give some examples in the following section. But if you want to take a look for yourself now, sign up for our 1-month full-access free trial. |
Just remember, when selecting software and online therapy platforms for managing depression treatment plans, not every program will be a good fit for your needs (or your clients’).
Important factors to consider before making a decision include ease of use, customization options, ability to track progress over time, integration with other systems, and cost.[10]
Treatment Plans for Depression in Quenza
The Quenza app is a full-featured, easy-to-use digital platform that helps you increase client engagement, scale your practice, and provide high-quality automated care.
To help you create and manage treatment plans for depression, our Expansions library is full of evidence-based exercises that can be used at any stage of a plan, including intake, assessment, active treatment, homework exercises, and evaluation.
Quenza even enables you to create Pathways for clients—a group of Expansions designed to focus on a particular issue in a predetermined sequence—that is ideally suited to depression treatment plans.
Let’s take a look at what a treatment plan for depression in Quenza might look like.
Step 1.
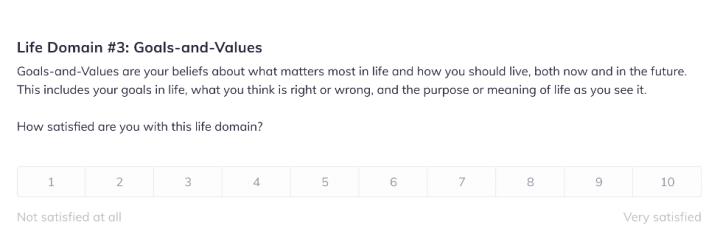
All good treatment plans for depression begin with an assessment. And while we always recommend completing a standardized depression measurement tool, most clinicians will also complete a further assessment of overall life satisfaction and functioning.
Our Life Domain Satisfaction Activity is the perfect place to start when working with a client experiencing depression.
The Life Satisfaction Activity starts with a brief overview.
Step 2.
After gaining some clarity around your client’s level of depression symptoms, life satisfaction, and areas of concern, it might be appropriate to discuss some treatment options. This might include things like medications, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes.
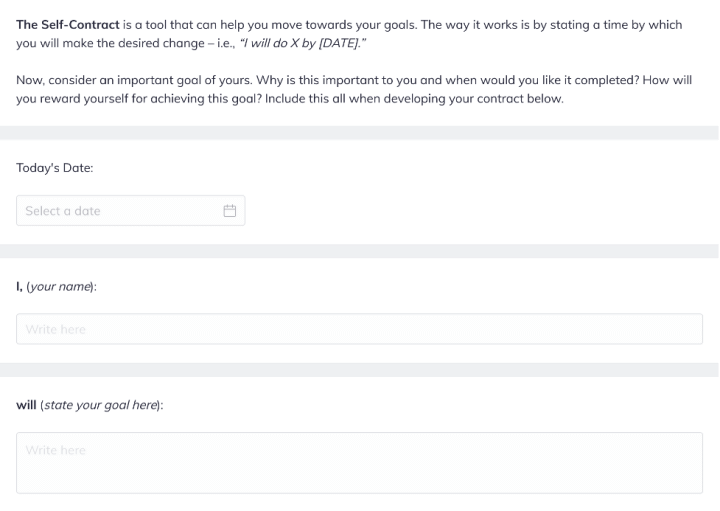
Once you’re clear on interventions, supporting your client to complete a self-contact can be a useful step.

This sets the tone for your work together. And ensures that your client makes a firm commitment to themself that they will treat their recovery with the respect it deserves.
We love self-contracts because they take the directiveness out of depression treatment, which can be an easy trap to fall into when a client is feeling particularly low and unmotivated.
Step 3.
Once it’s time to look at interventions in a treatment plan for depression, you’ll be able to pull from dozens of science-based therapy tools to use with your clients.
If CBT is an approach you often use, we’ve got Activities on all the major cognitive distortions, like this one on unhelpful thinking styles like Magnification and Minimization.

Or if you prefer interpersonal therapy, there are several ready-to-use Activities to help patients explore and work on their relationships.
One of our favorites is the Investing in Valued Relationships Activity.

And the Expansions library in Quenza also includes Activities on a range of lifestyle interventions that can be used in depression treatment plans, like mindfulness training and tools to support clients in becoming more physically active.

Step 4.
A critical, yet often overlooked part of depression treatment plans is feedback.
It’s essential to regularly ask clients how they are finding treatment, so you don’t waste precious time and resources on interventions that aren’t getting the expected results. But with everything else that’s going on during the session, it’s easy to let this slide.
To help with this issue, Quenza has Session Feedback Forms you can send to clients electronically in-between appointments, then review the results before the next session.

The Role of Technology in Depression Treatment
With the advent of modern technology, the landscape of mental health treatment has evolved significantly. Telehealth services and online therapy platforms have made mental health support more accessible than ever before, particularly for those living in remote areas or for individuals with mobility issues.
Apps designed to track mood, medication, and symptoms are also gaining popularity, offering patients a convenient way to manage their mental health. Furthermore, virtual reality (VR) is being explored as a tool for exposure therapy and other innovative treatment approaches. The integration of technology in mental health care not only enhances accessibility but also provides new avenues for intervention, which can be crucial in a comprehensive depression treatment plan.
The Importance of Family and Community Support
Family and community support play a critical role in the treatment and management of depression. A strong support system can provide emotional encouragement, practical assistance, and help individuals adhere to their treatment plans. Support groups and community resources can also offer a sense of belonging and understanding, which is vital for those battling depression.
Moreover, educating family members about depression and its effects can foster a more supportive home environment. Encouraging open communication and reducing the stigma associated with mental health issues are essential steps in ensuring that individuals receive the necessary support from their loved ones and community. This collective effort can significantly improve treatment outcomes and overall well-being.
Conclusion
Depression is a complex mental health disorder that comes in many forms and requires comprehensive, individualized treatment plans to effectively manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and prevent relapse.
Because the condition varies so much between individuals, it can be very time-consuming for mental health professionals to develop a unique plan for each of their clients.
Fortunately, technology has provided us with advanced tools to streamline the process of creating, implementing, and managing treatment plans for depression, ultimately improving outcomes for those living with this challenging condition.
To see how Quenza can help you create high-quality, evidence-based, personalized treatment plans for depression, sign up today for our 1-month full-access free trial for only.
Frequently Asked Questions
Treatment plans for depression should be reviewed regularly, typically every 4-6 weeks or more frequently if needed. The review process should assess progress towards goals, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and consider any changes in the patient’s circumstances or symptoms. If the patient is not showing improvement or is experiencing new challenges, the plan should be adjusted accordingly. Regular reviews ensure that the treatment remains responsive to the patient’s evolving needs and maintains its effectiveness over time.
A comprehensive depression treatment plan should include strategies for relapse prevention. This often involves educating the patient about early warning signs of depression, developing a personalized relapse prevention plan, and incorporating long-term maintenance strategies. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) techniques can be particularly useful in this regard, helping patients identify and challenge negative thought patterns that may lead to relapse. The plan might also include ongoing support through periodic check-ins or booster sessions, even after the acute phase of depression has been addressed.
Cultural competence is crucial in developing effective depression treatment plans. Different cultures may have varying perceptions of mental health, expressions of depressive symptoms, and preferences for treatment modalities. A culturally competent treatment plan takes into account the patient’s cultural background, beliefs, and values. This might involve adapting therapeutic techniques, considering traditional healing practices, or addressing culturally specific stressors. It’s also important to be aware of potential language barriers and the role of family in different cultures when formulating the treatment plan.
Digital health tools can be valuable components of a depression treatment plan when used thoughtfully. These might include mood tracking apps, online cognitive behavioral therapy programs, or telehealth platforms for remote therapy sessions. When integrating these tools, it’s important to consider the patient’s comfort level with technology, ensure data privacy and security, and use them as supplements to, not replacements for, in-person care. The treatment plan should clearly outline how these digital tools will be used, how data will be shared with the healthcare provider, and how they fit into the overall treatment strategy.
When a patient has co-occurring disorders alongside depression, such as anxiety or substance use disorder, the treatment plan needs to be more complex and integrated. It should address all disorders simultaneously, as they often interact and influence each other. This might involve a combination of therapies targeting different symptoms, careful medication management to avoid interactions, and a more intensive level of care. The plan should prioritize interventions that can address multiple issues at once, such as dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) for depression and borderline personality disorder. Regular communication between all healthcare providers involved is crucial to ensure a coordinated approach.
References
- ^ World Health Organization (2023) Depressive disorder (depression). Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression.
- ^ American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®). American Psychiatric Pub.
- ^ Jongsma, et. al. (2021) The Complete Adult Psychotherapy Treatment Planner. Wiley Publishing.
- ^ National Institutes of Mental Health (NIMH) What Is Depression. Retrieved 1st June 2023. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/depression#part_2257.
- ^ Cuijpers, P., Karyotaki, E., Weitz, E., Andersson, G., Hollon, S. D., van Straten, A. (2014). The effects of psychotherapies for major depression in adults on remission, recovery and improvement: a meta-analysis. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 204(5), 374-384.
- ^ Ströhle A. (2009). Physical activity, exercise, depression and anxiety disorders. Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996), 116(6), 777–784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-008-0092-x.
- ^ Pilkington, K., Kirkwood, G., Rampes, H., & Richardson, J. (2005). Yoga for depression: the research evidence. Journal of affective disorders, 89(1-3), 13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2005.08.013.
- ^ Cipriani, A., Furukawa, T. A., Salanti, G., Chaimani, A., Atkinson, L. Z., Ogawa, Y., ... & Efthimiou, O. (2018). Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs for the acute treatment of adults with major depressive disorder: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. The Lancet, 391(10128), 1357-1366.
- ^ Irish, L. A., Kline, C. E., Gunn, H. E., Buysse, D. J., & Hall, M. H. (2015). The role of sleep hygiene in promoting public health: A review of empirical evidence. Sleep Med Rev 23-36. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2014.10.001.
- ^ Salloum, A., Johnco, C., Lewin, A. B., McBride, N. M., & Storch, E. A. (2016). Barriers to access and participation in community mental health treatment for anxious children. Journal of affective disorders, 196, 54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2016.02.026.